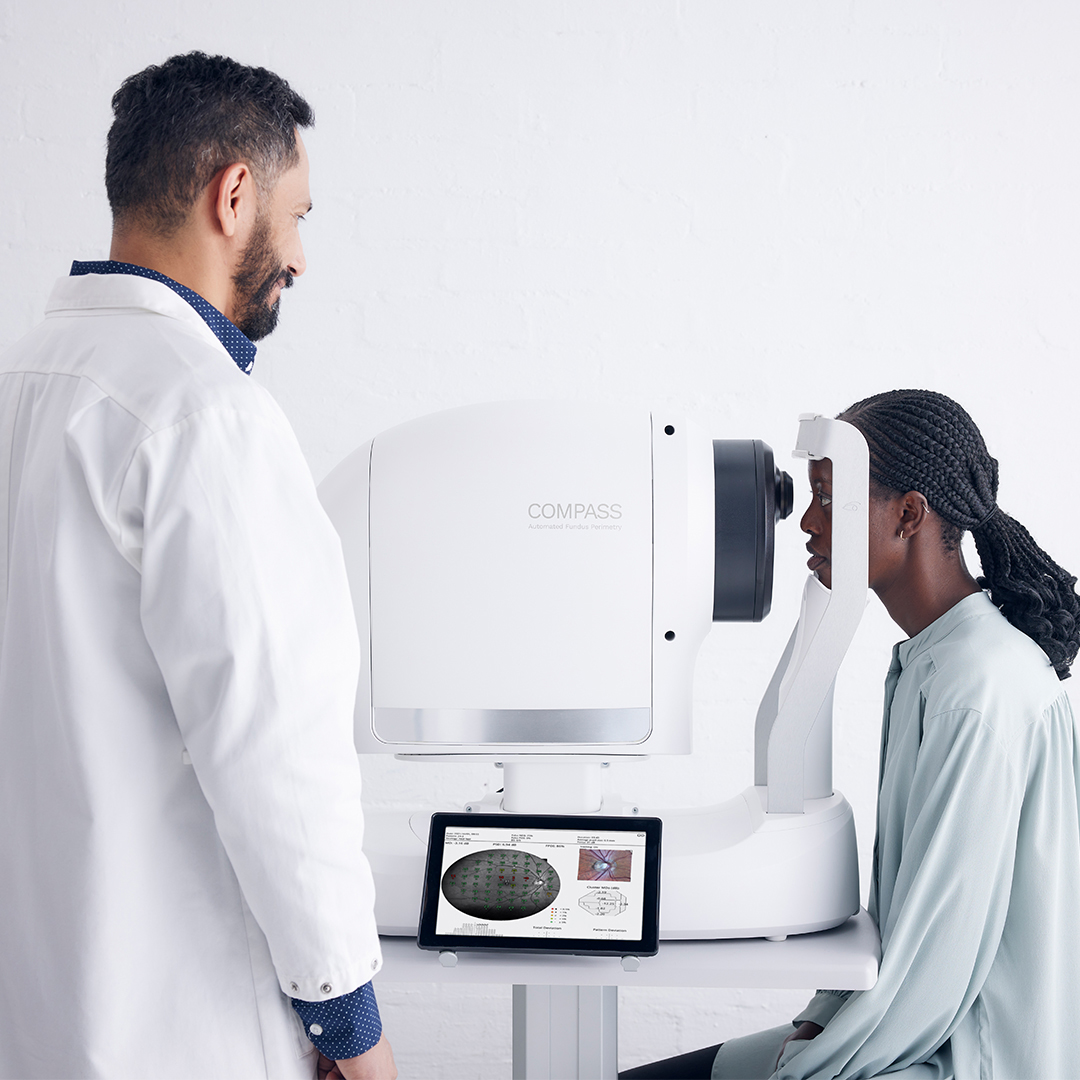
iCare COMPASS uses infrared retinal tracking to continuously monitor eye movements which includes blinking. Infrared images of the retina are captured at a high frequency of 25 times per second. This ensures the tracker can automatically reposition the perimetric stimuli based on the current eye position. Real-time compensation for fixation losses minimizes motion artifacts.
In conditions like glaucoma, it’s crucial to track pointwise progression and global indices trends over the years. The retinal tracker ensures low test-retest variability because the data always comes from the same anatomical locations, which is important for effective and reliable long-term monitoring of changes in a patient’s visual field.
For patients with an unstable fixation, the iCare COMPASS real-time retinal tracker can accurately identify and separate visual field defects. This is crucial for distinguishing between absolute scotoma areas and well-preserved vision, aiding in follow-up, and resolving fixation issues.
Additionally, the automated tracked perimetry combined with the simultaneous fundus imaging helps differentiate between glaucoma and other diseases by correlating structure and function. Using visual field tests, retinal tracking, and retinal images, the iCare COMPASS provides improved detection of retinal defects and diseases.
Unlike standard perimeters, the iCare COMPASS doesn’t rely on the objectivity of the operator when there is data loss or fixation instability. The tests can be carried out quickly without interruptions even if the patient blinks. The system seamlessly repeats lost stimuli without the patient’s awareness. Patients can also rest by closing their eyes and pulling away without risk of data loss.
Overall, the active retinal tracker benefits the patients providing a more accurate and efficient diagnostic process.
Share This News